Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease of the male prostate gland, located directly under the bladder and is a secondary part of the genitals.
Every 7 men over 35 suffers from prostatitis and with every naked risk of developing an inflammatory process in the prostate increases under the influence of external and internal factors.
Prostate inflammation can develop for various reasons, doctors distinguish the main one:
Distinguish the acute and chronic form of the disease.
Acute prostatitis is characterized by a sudden onset of the overall well -being, which is clinically accompanied by the following symptoms:
In the absence of diagnosis and timely treatment, acute prostatitis can be complicated by a purulent process and the release of pus from the urethra during urination.
In the transition of the disease to a chronic form of the course, the clinical signs of prostatitis disappear and the patient seems to be a recovery. The characteristic characteristics of the chronic inflammatory process in the prostate gland burn along the urethra with irradiation to the chat, which can be enhanced during urination and bowel movements. Gradually, the disease progresses and causes impotence. Chronic prostatitis implies periods of remission and exacerbation, but even at times of exacerbation, the symptoms will be wiped, not as pronounced as in acute form. The following symptoms appear clinically:
The chronic sluggish inflammatory process in the urethra irritates the nerve endings of the pelvis and causes constant urination, especially at night. Many men are embarrassed to see a doctor with such a delicate problem that increases the risk of developing such serious complications as complete erectile dysfunction, infertility and even prostate cancer.
In addition, by the focus of chronic infection in the prostate with blood flow and lymph, pathogens enter the kidneys, causing acute inflammation, retention of urine and increases the risk of kidney failure.
The constant accumulation of urine in the bladder and urethra creates favorable conditions for the formation of salts crystals, and then stones - very often prostatitis in men flows in parallel with urolithiasis.
The diagnosis, treatment and prevention of prostatitis is performed by a doctor urologist. To diagnose, determine the form and cause of the inflammatory process in the prostate gland, a number of examinations are prescribed:
If a pathological process is suspected of spreading the patient's pathological process, the patient is further performed by cystoscopy - examination of the walls of the bladder using a flexible device equipped with an optical system at the end.
When diagnosing prostatitis, it is very important to distinguish the pathological process from prostate adenoma and other urological diseases with a similar clinical course.
Treatment of acute and chronic form of prostatitis differs, so patients are strongly recommended not to self -confident.
The acute non -bacterial form of prostatitis is treated thoroughly with the help of herbal preparations and anti -inflammatory drugs.
The principles of therapy for the acute form of bacterial prostatitis directly depend on how pronounced the symptoms of the disease are.
A distinctive feature of bacterial prostatitis is acute onset and rapidly increasing signs of body intoxication - nausea, vomiting, headache, high body temperature. The process of emptying the bladder is accompanied by cutting pain in the lower abdomen and in the perineum, which are given to the lower back. Very often the purulent process joins and the abscess develops.
The treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis is performed in a hospital as the patient's condition can be extremely serious. Therapy consists in the complex approach:
Important! Prostate massage is strictly forbidden as the risk of sepsis is high.
Surgical intervention for prostatitis is only necessary if the patient develops a sharp slowdown in the urine and there is no way to empty the bladder. You cannot do without surgery in the case of an abscess of the prostate gland.
The course of treatment of prostatitis lasts for 14 days, after which the patient again conducts a comprehensive examination to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy. If necessary, the course of treatment is extended and adjusted.
The treatment of chronic prostatitis differs and largely depends on what stage of the course the pathological process is. In the case of exacerbation of the inflammatory process, therapy is similarly performed as in acute prostatitis.
The treatment of chronic prostatitis during remission is as follows:
In the phase of the inflammatory process of the patient's prostate, physiotherapy treatment is shown:
In neglected chronic prostatitis, the patient sometimes needs surgery. Can be done in two ways:
This method of surgical treatment refers to minimal invasive interventions, although it is performed with general anesthesia. During the procedure, a restectoscope is introduced under the urethra, through which the impulses of electric current are supplied. These electrical impulses act on the principle of electrical noise and partially remove the tissue of the prostate gland. A huge plus of this method of intervention is the lack of blood loss, as electrical waves not only remove the modified tissues of the prostate, but also immediately treat the blood vessels, preventing bleeding.
Transurethral resection greatly facilitates the patient's condition - after surgery, urination recovers, the man no longer burns in the crotch, he does not jump to the toilet at night. Erectile function and normal ejaculation are also restored. The whole process of surgery is controlled by a doctor on the monitor screen, so the risk of complications during surgery or as soon as it is minimal. 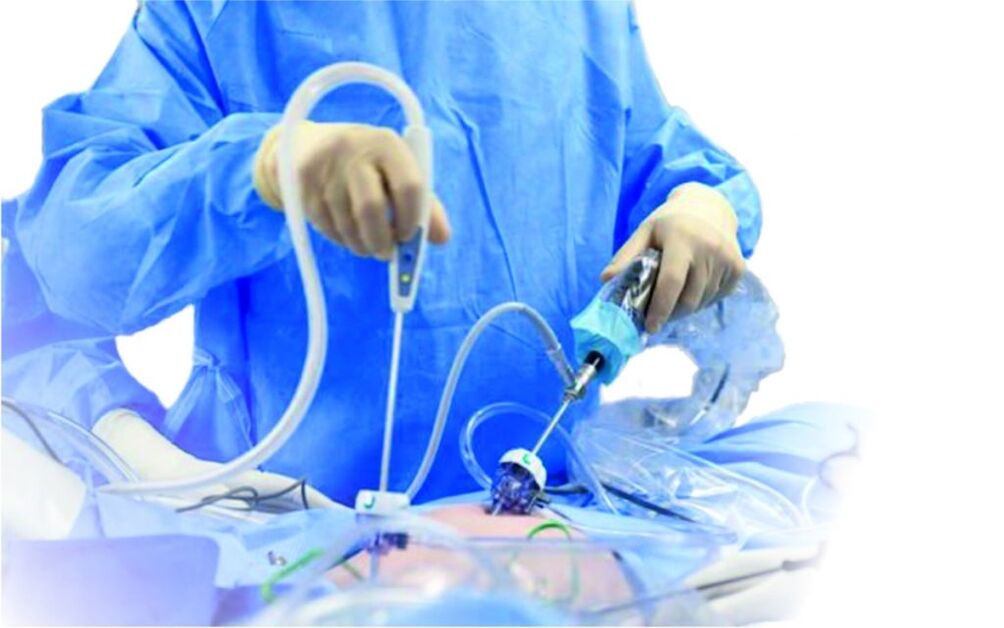
Prostatectomy is a serious abdominal surgery and is always associated with risks to the patient. During the surgery, the doctor completely eliminates the prostate gland or the greater part of it. The recovery period is 4-6 weeks, there is a high risk of developing postoperative complications, but sometimes this method of surgery is the only way to relieve the patient's condition and eliminate the effects of severe prostatitis.
Other methods of treating chronic prostatitis
Other methods of treating chronic prostatitis include:
In the absence of qualified therapy, prostatitis progresses quickly, enters the chronic form of current and threatens human health with its severe complications, including:
Sometimes for a long time prostatitis and chronic stagnant processes give impetus to the degeneration of the disease in adenoma and then prostate cancer.